The link between vitamin D and women’s immune response
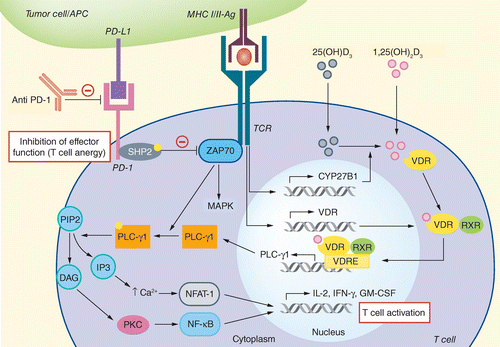
In recent years, there has been growing interest in understanding the impact of vitamin D on immune response. Vitamin D, also known as the sunshine vitamin, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Emerging studies suggest that it may have a particularly significant influence on women’s immune systems. This article explores the connection between vitamin D and women’s immune response, shedding light on the important role this nutrient plays in their overall health.
The Importance of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is unique, as it can be synthesized by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. It can also be obtained through certain foods and supplements. The main function of vitamin D is to aid in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, ensuring strong bones and teeth. However, research indicates that this vitamin goes beyond its well-known role in skeletal health and has a significant impact on the immune system.
Vitamin D and Women’s Immune Response
Scientific studies have revealed that vitamin D plays a vital role in modulating the immune response, and women appear to be particularly influenced by this nutrient. The female immune system is known for its ability to mount a robust response against pathogens, but it is also more prone to autoimmune diseases. Adequate levels of vitamin D have been associated with reduced risks of autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus.
Additionally, insufficient vitamin D levels have been linked to increased susceptibility to illnesses, including respiratory infections. Women who have low vitamin D may experience impaired immune function, making them more susceptible to infections and viruses. This is especially relevant for pregnant women, as they often have increased vitamin D requirements and need to ensure optimal immune system functioning for their own health and that of their developing baby.
Understanding the Mechanism
Researchers are still unraveling the precise mechanism by which vitamin D impacts the immune system. It is believed that vitamin D binds to specific receptors present on various immune cells, including T cells and B cells. This interaction helps regulate the immune response by promoting an appropriate balance between the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory actions. Vitamin D also supports the production of antimicrobial peptides, which are essential for fighting off infections.
Furthermore, vitamin D enhances the communication between immune cells, improving their ability to coordinate a strong defense against harmful pathogens. Women with sufficient vitamin D levels may experience enhanced immune surveillance and a more effective defense against potential threats.
Sources of Vitamin D
There are several ways to ensure adequate vitamin D levels. The primary source is sunlight, as the skin’s exposure to UVB rays stimulates vitamin D synthesis. However, factors such as location, weather conditions, and sunscreen use can affect the amount of vitamin D produced. Foods rich in vitamin D include fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, fortified dairy products, eggs, and mushrooms. Supplementation is another option, specifically during winter months or for individuals who have limited sun exposure.
Conclusion
Vitamin D plays a multifaceted role in women’s immune response. From enhancing immune cell communication to promoting an appropriate balance between inflammation and immune defense, it is clear that this nutrient is vital for overall health and well-being. Maintaining sufficient vitamin D levels is crucial, particularly for women who have a higher susceptibility to immune-related disorders. Adequate sun exposure, dietary choices, and supplementation can all contribute to supporting a strong and robust immune system in women.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet or supplement routine.





