The link between gut microbiota and women’s immune health
Gut microbiota, the complex community of microbes that resides in our digestive system, plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and immune function. Recent studies have shown a fascinating connection between gut microbiota and various aspects of women’s health, including their immune health. In this article, we will explore this link and delve into the importance of a healthy gut microbiome for women.
Gut Microbiota: The Basics
Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, collectively known as gut microbiota. These microscopic organisms coexist with us in a symbiotic relationship, influencing various aspects of our health, including digestion, metabolism, and immune function.
The Immune System and Women’s Health
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens and maintain overall well-being. In women, the immune system plays a crucial role in maintaining reproductive health and protecting against infections.
The Gut-Immune Axis
Research has revealed a bidirectional relationship between gut microbiota and the immune system, referred to as the gut-immune axis. The gut microbiota helps shape and educate the immune system, while the immune system regulates and maintains a balance in the gut microbial community.
Gut Microbiota and Immune Regulation
The gut microbiota influences the development and maturation of immune cells, such as T cells and B cells, helping to maintain a balanced and efficient immune response. Certain microbes in the gut produce metabolites that have immunomodulatory properties, influencing the behavior of immune cells and their response to pathogens.
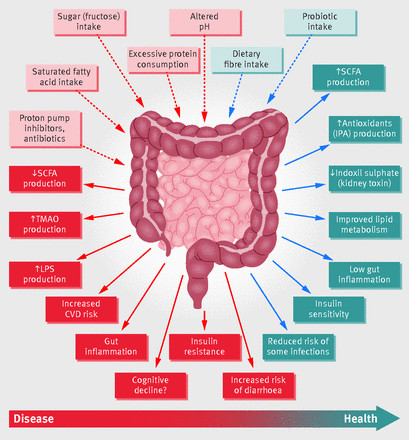
Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Response
An imbalance in the gut microbiota, also known as dysbiosis, can lead to increased inflammation within the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to various diseases, including autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and even certain types of cancer. A healthy gut microbiome helps regulate inflammation, thereby supporting a balanced and controlled immune response.
Women’s Immune Health and Gut Microbiota
Several studies have shown that gut microbiota influences women’s immune health in unique ways. Here are some key findings:
Reproductive Health
Research suggests that a healthy gut microbiome can positively influence reproductive health in women. Certain gut microbes are involved in the metabolism of estrogen, a hormone essential for proper reproductive function. Imbalances in the gut microbial composition may disrupt estrogen metabolism and lead to menstrual irregularities, fertility issues, and even complications during pregnancy.
Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common in women and can be recurrent. Studies have found that a diverse and balanced gut microbiota can help prevent UTIs by enhancing the immune response in the urinary tract and inhibiting the growth of uropathogenic bacteria.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, are more prevalent in women. Growing evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis may contribute to the development and progression of these conditions. A disturbed gut microbiota can trigger an abnormal immune response, leading to chronic inflammation and autoimmune reactions.
Weight Management and Metabolic Health
A healthy gut microbiome is also crucial for weight management and metabolic health in women. Certain gut microbes influence energy extraction from food, fat storage, and hormonal regulation. An imbalance in gut microbiota, often observed in conditions like obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), may contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and metabolic imbalances.
Maintaining a Healthy Gut Microbiota
To support women’s immune health and overall well-being, it is essential to nurture a healthy gut microbiota. Here are some tips:
Dietary Strategies
Include a variety of fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, in your diet. These act as prebiotics, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Additionally, fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut contain live cultures of beneficial bacteria, which can help replenish and diversify gut microbiota.
Probiotic Supplements
In certain cases, probiotic supplements may be beneficial in restoring and maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable probiotic strains for your specific needs.
Lifestyle Factors
Regular exercise, stress management techniques like meditation or yoga, and adequate sleep contribute to a healthy gut microbiota. Chronic stress and disrupted sleep patterns may negatively impact the gut microbial composition and immune response.
Antibiotic Use
Use antibiotics judiciously, as they can disrupt the balance of gut microbiota. If you require antibiotics, discuss with your healthcare provider whether probiotics may be recommended concurrently to minimize potential disturbances.
Conclusion
The connection between gut microbiota and women’s immune health is undeniable. A diverse and balanced gut microbial community plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses, maintaining reproductive health, and protecting against various infections and diseases. By adopting strategies to support a healthy gut microbiome, women can enhance their immune health and overall well-being.