The impact of alcohol on women’s hormonal balance
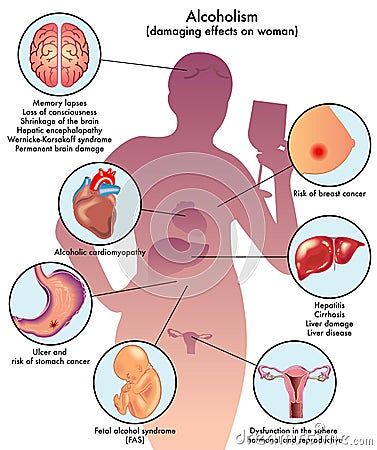
The female hormonal system plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Hormones regulate a wide range of bodily functions, including metabolism, reproduction, mood, and sleep patterns. Any disruption in hormonal balance can have profound effects on a woman’s physical and emotional health.
Alcohol Consumption and Hormonal Health
Alcohol is a widely consumed beverage, and its impact on hormonal health is a subject of growing concern. While moderate alcohol consumption might not pose significant risks to overall health, excessive or chronic alcohol intake can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance within a woman’s body.
The Effects of Alcohol on Estrogen Levels
Estrogen is a primary hormone in women, responsible for regulating menstrual cycles, maintaining bone density, and supporting reproductive health. Alcohol consumption can affect estrogen levels in several ways. Studies have shown that alcohol can increase estrogen production primarily by disrupting the metabolism of estrogen in the liver. Elevated estrogen levels can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, decreased fertility, and an increased risk of certain hormone-related cancers.
Alcohol’s Influence on Progesterone
Progesterone is another vital hormone in women, involved in supporting pregnancy, promoting healthy sleep patterns, and balancing the effects of estrogen. Alcohol consumption can disrupt the production of progesterone, leading to imbalances between estrogen and progesterone ratios. This hormonal imbalance can contribute to menstrual irregularities, mood swings, and increased vulnerability to anxiety and depression.
Impact on Thyroid Function
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall hormonal balance. Alcohol abuse has been linked to an increased risk of thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism. An underactive thyroid can result in weight gain, fatigue, and mood disturbances, significantly impacting a woman’s overall well-being.
Alcohol and Stress Hormones
Excessive alcohol intake can also trigger the release of stress hormones like cortisol. Increased cortisol levels can disrupt normal sleep patterns, increase feelings of anxiety and depression, and lead to weight gain, especially around the abdominal area. Chronic stress hormone elevation can further exacerbate existing hormonal imbalances in women.
Caring for Hormonal Balance
It is essential for women to be mindful of their alcohol consumption and its potential impact on hormonal balance. Moderate alcohol intake, defined as one drink per day, is generally considered safe for most women. However, those already experiencing hormonal imbalances or seeking to optimize their reproductive health may benefit from abstaining from alcohol altogether.
Conclusion
The impact of alcohol on women’s hormonal balance is a complex subject that requires careful consideration. While occasional or moderate alcohol consumption may not significantly affect hormonal health, excessive or chronic drinking can lead to imbalances in estrogen, progesterone, thyroid, and stress hormones. Prioritizing hormonal balance by making informed choices about alcohol consumption is crucial for women looking to optimize their overall well-being.




