Navigating hormonal changes in women with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
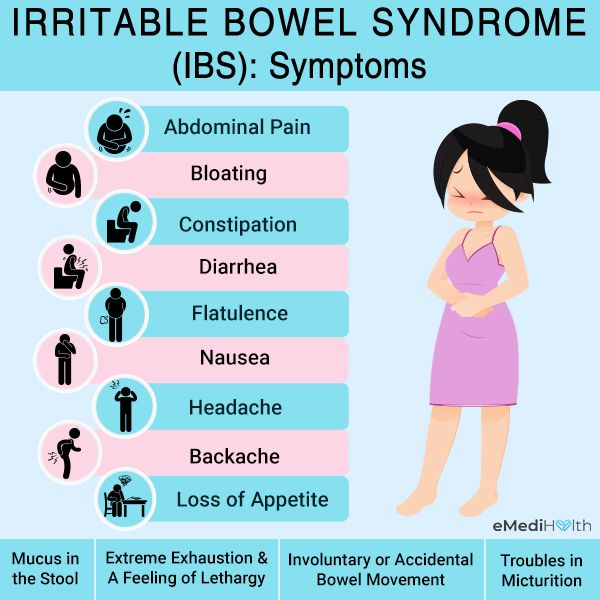
Women with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) often face additional challenges due to hormonal changes that occur throughout their menstrual cycle. IBS is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea or constipation, and an overall impact on quality of life. While the exact cause of IBS remains unknown, researchers have identified a clear link between hormonal fluctuations and symptom severity.
The Menstrual Cycle and IBS
Many women with IBS experience changes in their symptoms during the different phases of their menstrual cycle. These fluctuations are believed to be connected to hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen has been found to stimulate bowel movements and may increase sensitivity in the gut, while progesterone can have the opposite effect, slowing down the movement of the intestines.
During the premenstrual phase, when progesterone levels rise, some women experience an increase in IBS symptoms such as constipation, bloating, and abdominal pain. On the other hand, during the menstrual phase, when both estrogen and progesterone levels drop significantly, symptoms may improve for some women. However, it’s important to note that every woman’s experience with hormonal fluctuations and IBS can vary.
Navigating Hormonal Changes and Managing IBS
While it may be challenging to completely eliminate the impact of hormonal changes on IBS symptoms, there are strategies that can help women navigate these fluctuations and manage their condition effectively:
Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle: Keep a record of your menstrual cycle and IBS symptoms to identify any patterns or correlations. This information can be valuable in understanding how hormonal changes affect your condition and planning accordingly.
Lifestyle Modifications: Making certain adjustments in your lifestyle can help alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal changes. Regular exercise, stress reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation, and a balanced diet rich in fiber can contribute to better overall gut health.
Medication Management: Speak with your healthcare provider to explore potential medication options that may help in managing IBS symptoms during specific phases of your cycle. Hormonal medications or specific gastroenterological medications can be prescribed as appropriate.
Dietary Modifications: Some women may find that modifying their diet during specific phases of their menstrual cycle can help manage symptoms. Reducing caffeine, minimizing processed foods, and avoiding trigger foods can be beneficial in reducing gastrointestinal distress.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If you are a woman with IBS struggling to navigate hormonal changes and experiencing severe symptoms, it is important to seek professional guidance. Consulting with a gastroenterologist or a healthcare provider specializing in women’s health can help devise an effective management plan tailored to your specific needs. They can offer personalized advice, conduct necessary diagnostic tests, and provide medication recommendations to help alleviate symptoms.
Navigating hormonal changes in women with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) requires understanding the complex relationship between hormone fluctuations and gastrointestinal symptoms. By tracking your menstrual cycle, adopting lifestyle modifications, considering medication management, and making dietary adjustments, you can empower yourself to better manage your IBS and improve your quality of life.





